New National Education Policy 2022
What is the New National Education Policy (NEP)?
The New National Education Policy or the NEP is a new education policy that the government has rolled out, to change certain outdated aspects of the old education system and have a structure that reduces student load and is suited to the changing times. The NEP is a framework for education from elementary level to higher secondary level, for rural as well as urban areas. This policy was approved on 29th July 2020 by the Union Cabinet, and is replacing the educational policy which was made in 1986, almost 25 years ago. The NEP has been finalised and is in the process of implementation. Over the next few years the education boards of all the states will slowly implement the changes outlined in the policy.
What is the main objective of NEP?
The NEP was launched to completely overhaul India’s current educational framework that has been declared as outdated by many academics and educators. The old policy, which was made decades ago is no longer viable in a world that is so fast-changing. Innovations in technology and teaching methods, changes in curriculum for school, as well as the increasing focus on the students’ wellbeing all needed to be taken into consideration. The NEP was made to shift focus from only academics to vocational subjects as well to create a comprehensive curriculum. Furthermore, there has been added stress on learning regional languages in the new policy.
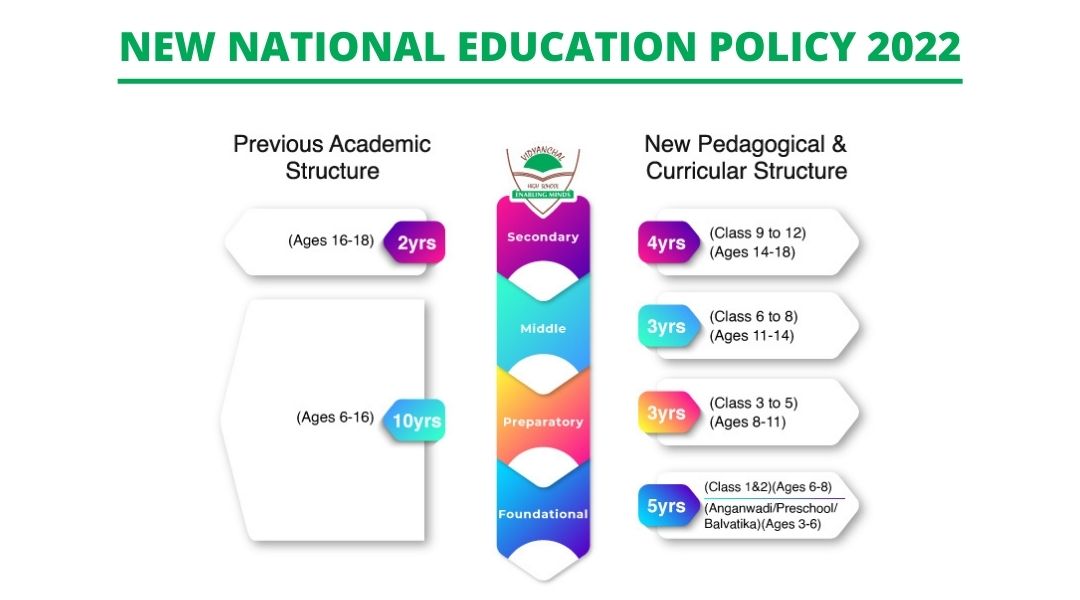
New structure of schooling under NEP
The major change that the NEP would bring about is a total transformation of the structure of schooling. Until now, schools in India followed a 10+2 system, wherein students would appear for board exams in the 10th grade, after the end of school and 12th grade, after the end of Junior college. However, as per the new policy, the structure has been changed to 5+3+3+4. This means that schooling has been divided into four stages rather than two. Here is a breakdown of the four stages:
- Foundation stage – This is the stage that includes grades like playgroup or nursery, pre-primary or kindergarten grades as well as 1st and 2nd grade. The age group for this stage is 3 to 8 years and the focus would be on activity based learning and basic literacy skills.
- Preparatory stage – This stage includes 3rd, 4th and 5th grades, and is for the age group of students from 8 to 11 years. This is the stage where students would slowly be introduced to more advanced subjects like art, science, maths, etc. However, there would still be extra attention given to reading, writing, and physical education.
- Middle stage – This stage, covering classes 6th, 7th and 8th is the transitional phase between elementary and secondary education. Students would be in the age group of 11 to 14 years. Subjects like maths, science and languages would be taught alongside more varied subjects falling under arts, humanities, social sciences, etc.
- Secondary stage – The last stage in this structure is secondary education, from class 9th to 12th, with students falling in the age group of 14 to 18 years. This stage would further be divided into two phases, of two years each. This stage is meant to prepare students for higher education of their choice.
Other Major Changes
- The NEP is characterised by holistic education right from the pre-primary stage, where focus will be laid on activity based learning and later, on vocational training, along with usual academics.
- According to the NEP, regional languages will be given extra importance in education, and each state can implement the changes as deemed appropriate by them. Furthermore, ancient languages or foreign languages will also be offered to students.
- The weight of school bags will be reduced by 10% and there will be digital weighing machines at all schools to ensure that the load is not too high.
- There would be no demarcation of streams such as science, commerce and arts in 11th and 12th grade, and students would be free to choose from different disciplines as per their choice.
- Digital learning, and technological teaching equipment would be introduced to all schools. Students would be taught to code from 6th grade. Overall, the syllabus would be in tune with the current technological advances.
